Watershed Delineation Using HEC-HMS GIS Tools (Part 2 of 3)
After a watershed has been delineated using HEC-HMS GIS tools, the subbasins and reaches can be further refined using HEC-HMS merge and split functions. Five subbasins and two reaches were delineated in this post and now we want to merge Subbasin_3, Subbasin_4 and Subbasin_5, as well as R_1 and R_2 reaches. Subbasins and reaches must be adjacent to each other for the merge operation to work. Subbasins can be side-by-side adjacent (if the merge produces a logical single outlet) or upstream-downstream so that the outlet for the merged sub-basin is the same as the lower subbasin. Reaches should have an upstream-downstream relationship. Two ore more elements can be merged at one time, even though the following example demonstrates merging two elements only.
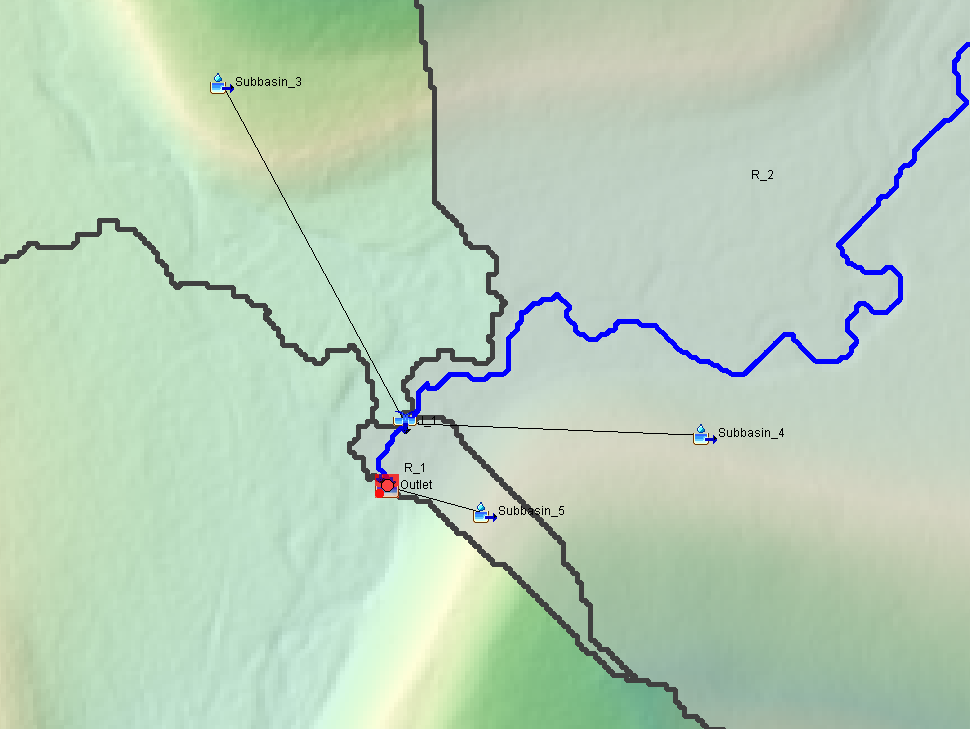
- First to merge Subasin_4 and Subasin_5: Make sure the mouse cursor is a pointer (or arrow), select Subasin_4 by clicking it on Basin Model Map View window; Holding down the CTRL key, select Subasin_5 and now both subbasins should be highlighted as shown on Figure 1. Click top menu of GIS, then Merge Elements to combine the two selected subbasins. A new subbasin Subbasin_6 is created to replace Subbasin_4 and Subbasin_5 (Figure 2).
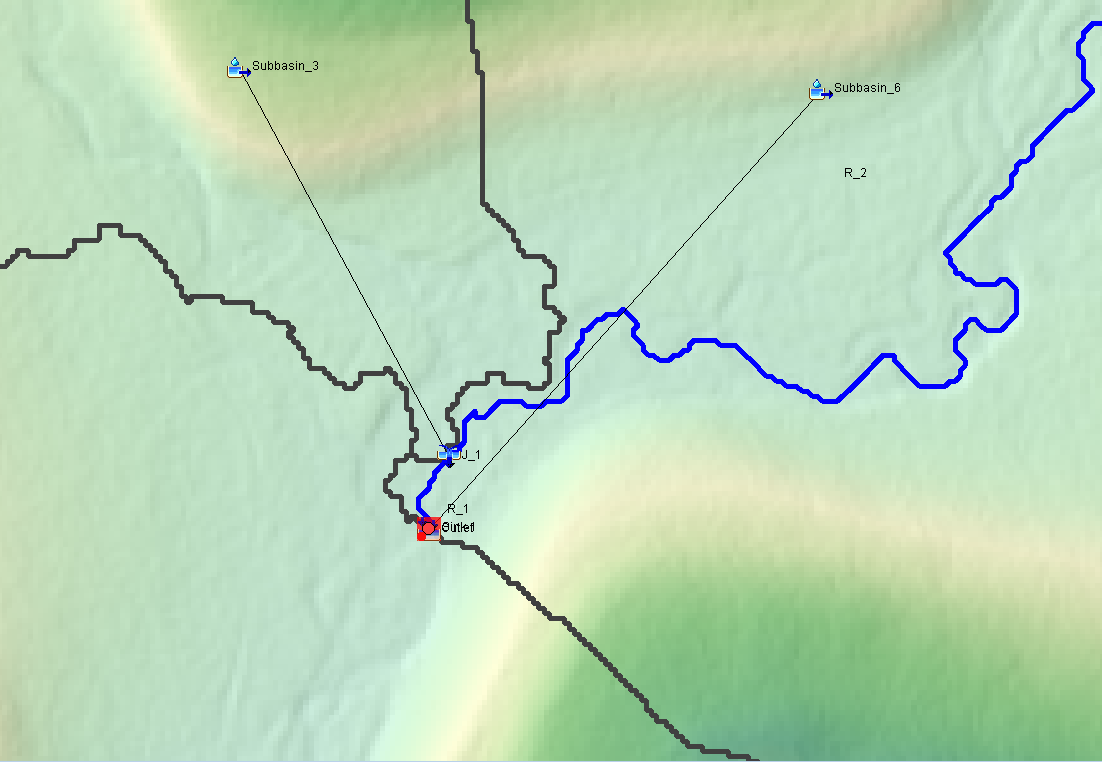
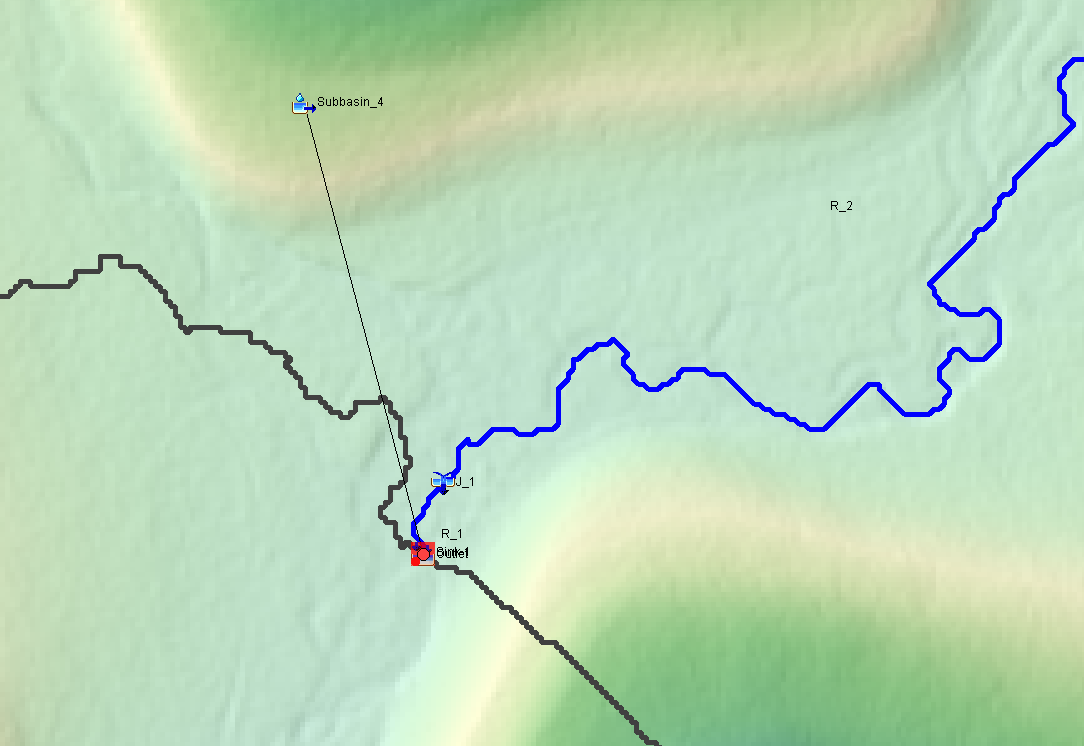
- Select Subbasin_6 and Subbasin_3 to merge them to create a new subbasin Subbasin_4 (Figure 3). It should be noted that this new Subbasin_4 is the combination of the original Subbasin_3, Subbasin_4, and Subbasin_5.
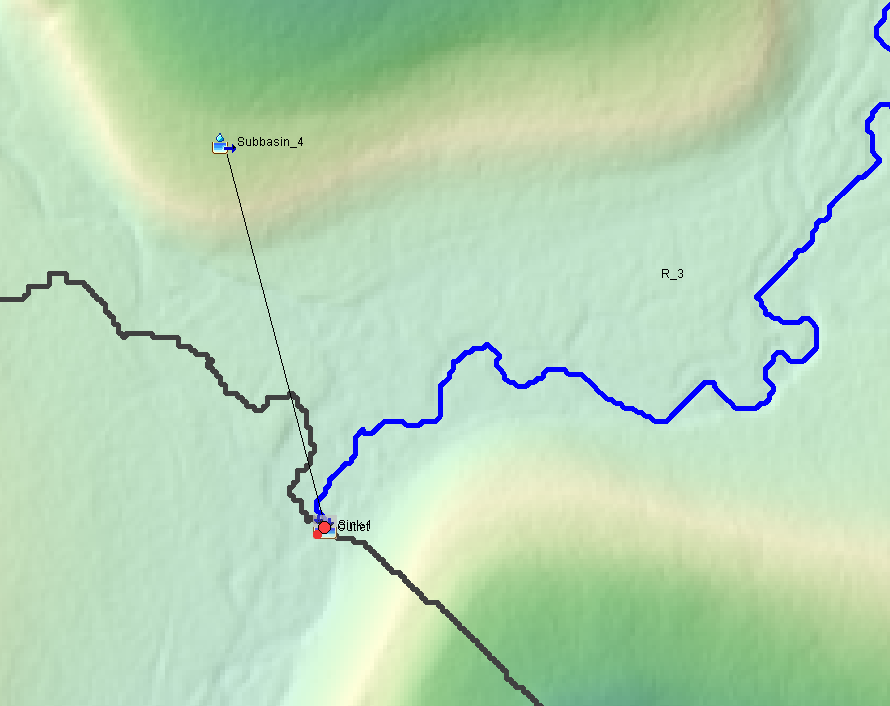
- Since the original Subbasin_3, Subbasin_4, and Subbasin_5 have been merged to a newly created subbasin Subbasin_4, Reach R_2 does not need to be a separate reach anymore and can be merged with R_1. Select R_2 and R_1, and then click top menu of GIS, then Merge Elements to combine the two selected reaches as a new Reach R_3 (Figure 4). The junction of J_1, which is to connect R_1 and R_2, is also eliminated due to the merging. Sometimes, junctions will still be present after merging and you will need to delete them manually if they are not part of the basin networks anymore.
- Click top menu of Parameters, then Characteristics —> Subbasin and Reach to re-calculate/update subbasin and reach characteristics parameters such as subbasin longest flowpath length, longest flowpath slope, and reach sinuosity. Make sure the filter set as “None” to calculate and display all subbasins and reaches.
- Now we will demonstrate HEC-HMS Split Element capability. First make sure the Identified Streams layer is visible (menu View —> Map Layers…). Select/highlight the Subbasin_1 and click top menu of GIS, then Split Element. You will notice your mouse cursor becomes a crosshair. Click on a desired location to split Subbasin_1, which should be located exactly on top of an identified streams grid cell. You need to zoom in far enough to click within an identified stream grid cell. The original Subbasin_1 is split into new Subbasin_1 and Subbasin_3 and a new Reach R_1 is also created to accept the outflow from Subbasin_1 and then route the flow downstream to Junction J_2 (Figure 5). At J_2, outflows from Subbasin_2 and Subbasin_3 are combined with R_1 flow before being carried and routed by Reach R_3.
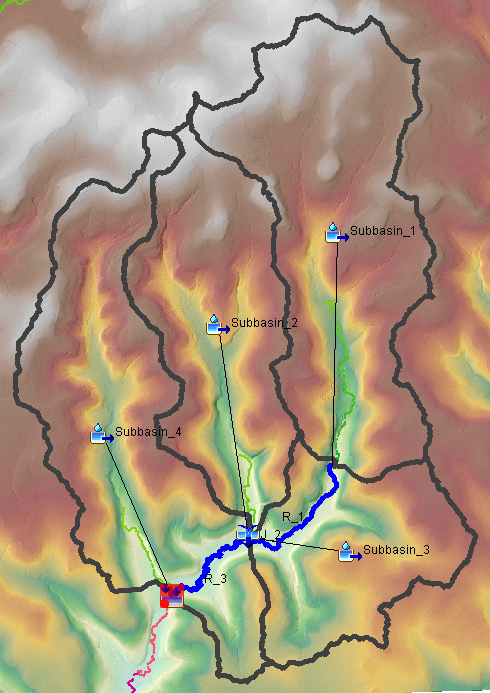
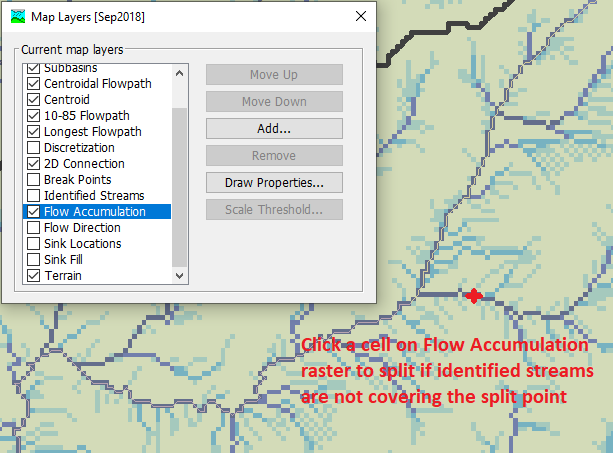
In case that the identified streams do not cover the desired split area, you can either re-run the Identify Streams command using a smaller threshold value, or simply turn on the flow accumulation layer and use the flow accumulation raster grid as a background to pin down the split point.
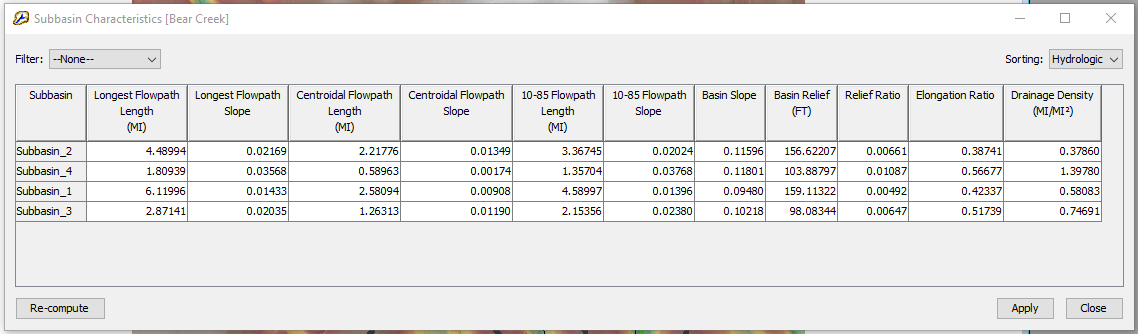
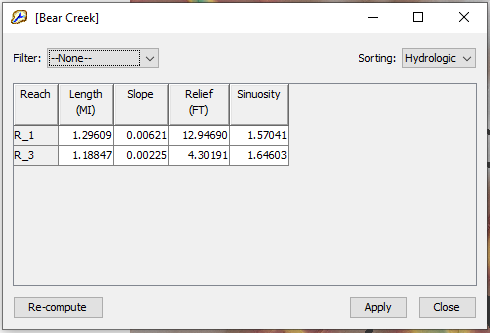
- Click top menu of Parameters, then Characteristics —> Subbasin and Reach to re-calculate/update subbasin and reach characteristics parameters such as subbasin longest flowpath length, longest flowpath slope, and reach sinuosity (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Make sure the filter set as “None” to calculate and display all subbasins and reaches.
- Save the completed HEC-HMS project and go to the Post 3 of 3 for HEC-HMS hydrology parameter estimation.
Leave a Reply