Green-Ampt Infiltration Method and Parameter Estimation
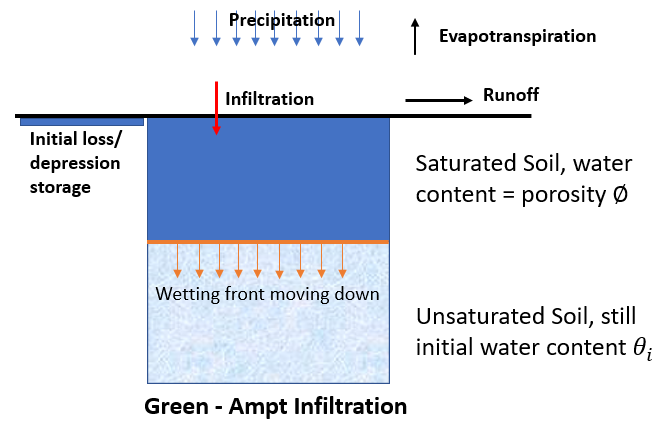
As a theory-based infiltration method, Geen-Ampt is widely used in hydrologic modeling since its parameters are easy to acquire, especially for those project sites without monitored data for model calibration. Green-Ampt method was initially developed for ponded infiltration into a homogeneous soil with a uniform initial water content and the water wetting front movement in the soil was governed by Darcy’s law (Figure 1).
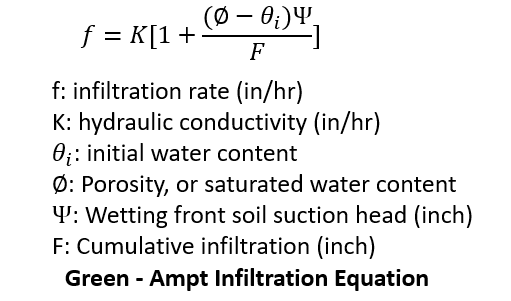
As shown in Figure 2, generally four (4) parameters are required for Green-Ampt infiltration method: initial water content (dimensionless), saturated water content or porosity (dimensionless), wetting front soil suction head (inch), and hydraulic conductivity (in/hr). Some literatures and software list three (3) parameters by combining initial water content and saturated water content as a single parameter – initial water content deficit (saturated water content – initial water content)
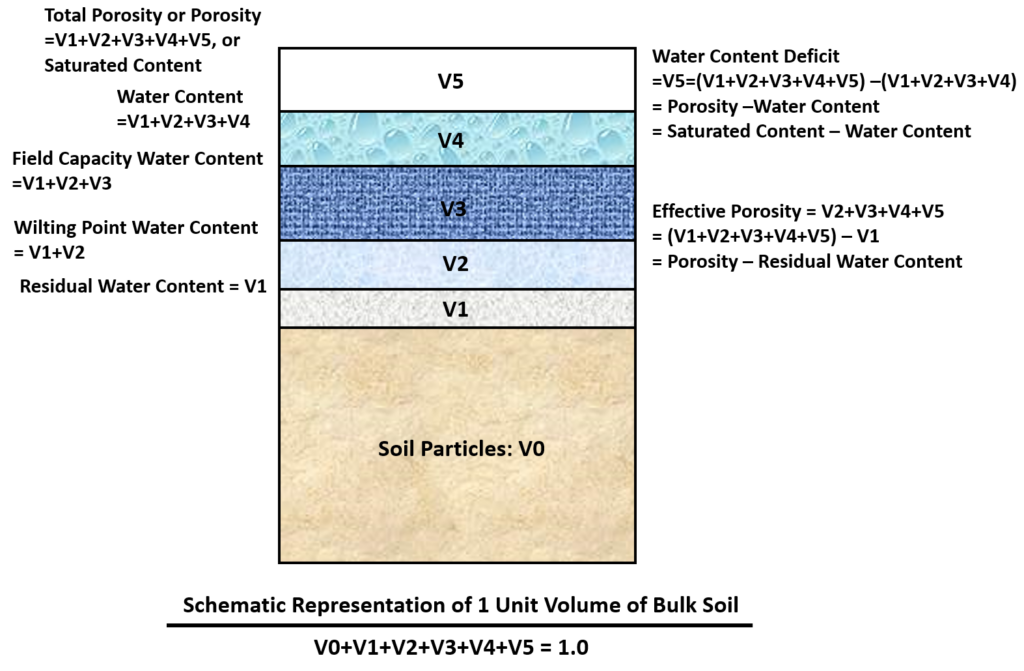
Soil Water Content or Moisture Content is the fraction of the total soil volume is taken up by water which is a dimensionless value expressed as the ratio of V-water to V-bulk soil. The corresponding value at the commencement of a simulation is called initial water content, or simply initial content. When the soil is saturated, the water content is called saturated water content and it can be estimated as porosity or total porosity.
The initial water content usually can not be zero in reality because of residual soil water/moisture content which is the water content of a soil where a further increase in negative pore-water pressure does not produce significant changes in water content. By definition, the residual soil water content (Unit: dimensionless, V-water/V-bulk soil) represents the remaining water content after a saturated soil is allowed to drain thoroughly for an extended period of time. Depending on antecedent moisture conditions (AMC), the initial water content is a value between residual water content and saturated water content, and correspondingly the initial water content deficit can range from zero (with saturated water content) to effective porosity (with residual water content).
Under the average antecedent moisture condition (average AMC), Dr. David Maidment in his book of Handbook of Hydrology suggested using wilting point (-1500 kPa water content) as initial water content in the western USA and using field capacity (-33kPa water content) as initial water content in the eastern USA. Correspondingly, the initial water content deficit will be calculated as (porosity – wilting point, Do NOT use effective porosity here – see Figure 3 for illustration) for Western USA or (porosity – field capacity) for Eastern USA for average AMC (Table 2). For the concepts of wilting point and field capacity, refer to this post.
Wetting front suction head (inch) and hydraulic conductivity (in/hr) of various soil textures were estimated by Rawls in 1982 and 1983 (Table 1, after unit conversion). Rawls stated in his 1983 paper that the Green-Ampt hydraulic conductivity is one-half the saturated hydraulic conductivity presented in the 1982 paper. For Green-Ampt infiltration method, the hydraulic conductivity values from the 1983 paper (B) are recommended as initial estimation, which are also endorsed by HEC-HMS Tutorials and Guides and EPA SWMM User’s Manual.

In addition to the four required parameters mentioned above, when applying Green-Ampt infiltration method for HEC-RAS 2D modeling in a 2D infiltration layer, two more parameters are needed as shown in Figure 4: 1. residual moisture content, or residual soil water content; and 2. pore-size distribution index. Both of the parameters are dimensionless.
Per HEC-RAS 6.1 User’s Manual, the two additional Green-Ampt parameter are required to utilize the Green-Ampt with Redistribution (GAR) method. The residual moisture content, or residual soil water content and pore-size distribution index are summarized in Table 2.

EPA SWMM version 5.1.010 (2015) adopted a Modified Green-Ampt method which will not reset the soil moisture deficit and cumulative infiltration values when the upper zone is unsaturated and the rainfall rate is less than the Hydraulic Conductivity K. The Modified Green-Ampt method will end up with more infiltration for storm events that begin with low rainfall intensities, for example, the SCS rainfall distributions. It appears EPA encourages the use of the Modified Green-Ampt method and the original Green-Ampt method is only kept in SWMM to maintain backwards compatibility.
A comparison between the the two Geen-Ampt methods was made (Suction Head 3.5 inch, Conductivity 0.35 in/hr, and Initial Deficit 0.35; The rest of the subcatchment parameters are the same: area 6.4 ac, width 500ft, slope 0.5%, 0% Imperv, N Perv 0.1, Runoff method – SWMM Nonlinear Reservoir Routing). As predicted, the subcatchment with the Modified Green-Ampt method produces more infiltration and less runoff (Figure 5).
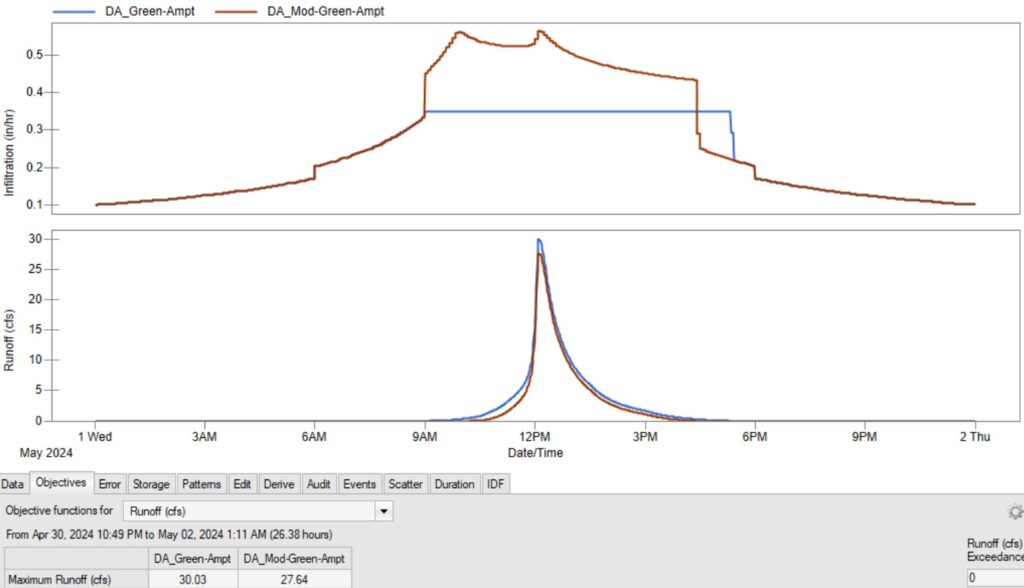
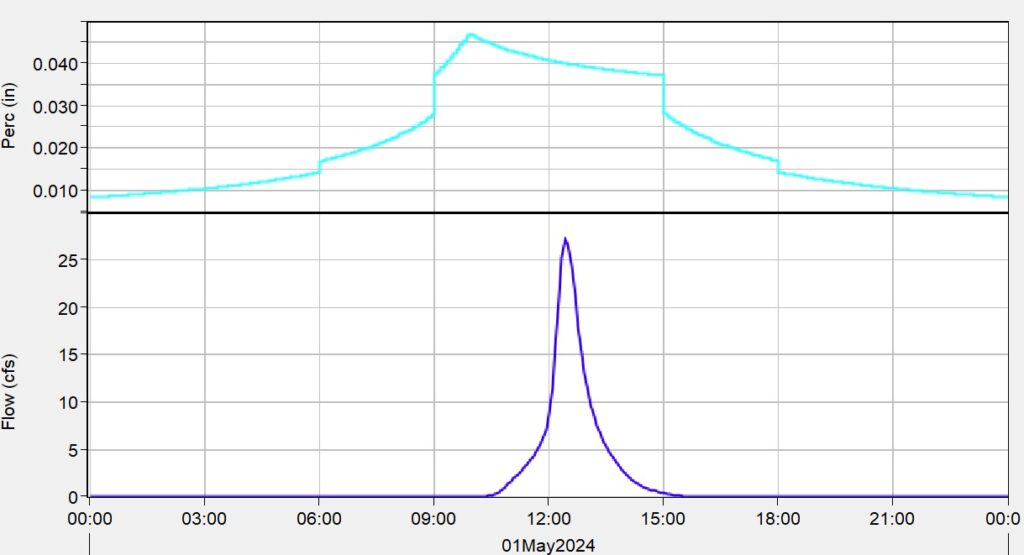
Furthermore, a HEC-HMS model was established to test which Green-Ampt method is implemented by HEC-HMS. There is no direct comparison between HEC-HMS and EPA SWMM models since HEC-HMS can not apply the SWMM Nonlinear Reservoir Routing method for runoff transformation, but judging by the shape of the HEC-HMS infiltration curve, it is likely that HEC-HMS uses a method similar to the EPA’s Modified Green-Ampt method (Figure 6).
According to the study done by Tuflow, Green-Ampt infiltration method is relatively insensitive to porosity (saturated water content) and wetting front soil suction head. During model calibration, the focus should be on hydraulic conductivity and initial water content. The hydraulic conductivity impacts the runoff volume greatly: the higher the hydraulic conductivity, the more infiltration and the less runoff. When initial water content is increased, the model has a quick response to rainfall and usually ends up with more runoff. The influence of the initial water content tends to be less substantial after soil becomes saturated.
Green-Ampt infiltration method is available in InfoWorks ICM for both of its hydrology methods – the traditional subcatchment hydrology method and Rain-on-Grid on a 2D zone.
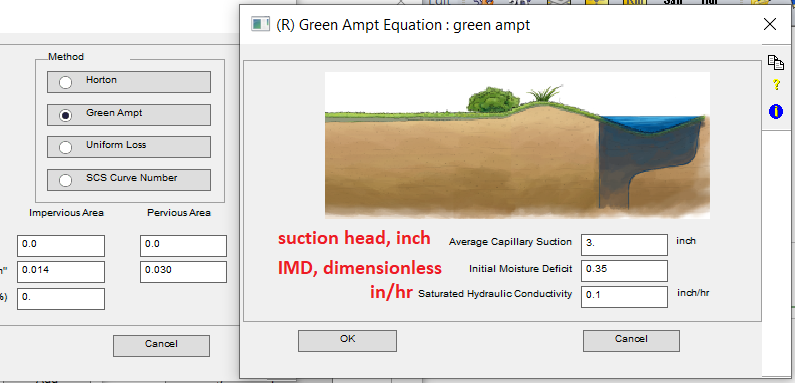
In XPSWMM, Green-Ampt infiltration method needs to be defined in Global Data… –> (R) Infiltration (Figure 7).
PS. PCSWMM help page has a soil characteristics table (Table 3) which generally matches Table 1 and Table 2 above. In Table 3, the Initial Deficit is estimated as the difference between Porosity and Wilting Point.

6 COMMENTS